CRISPRon-BE(v1.1): CRISPR-Cas9 base editing guide design
About
The CRISPRon-BE webserver is dedicated to design gRNAs for CRISPR/Cas9-derived base editing experiments. The models implemented in the webserver can predict on-target gRNA editing effciency and the resulting outcomes by base editors. Currently, our webserver supports two types of base editor predictions: adenine base editors (ABE, converting A:T base pairs to G:C base pairs) and cytosine base editor (CBE, converting C:G base pairs to T:A base pairs). The model designed for ABE (CRISPRon-ABE) is trained on data from ABE7.10 and ABE8e, while the model for CBE (CRISPRon-CBE) is trained on data from BE4. Using our webserver, you can obtain not only the predicted editing efficiency of the designed gRNAs but also their potential bystander effects from base editors.
Details on how to use the webserver and descriptions of the input and outputs are given in the Help page.
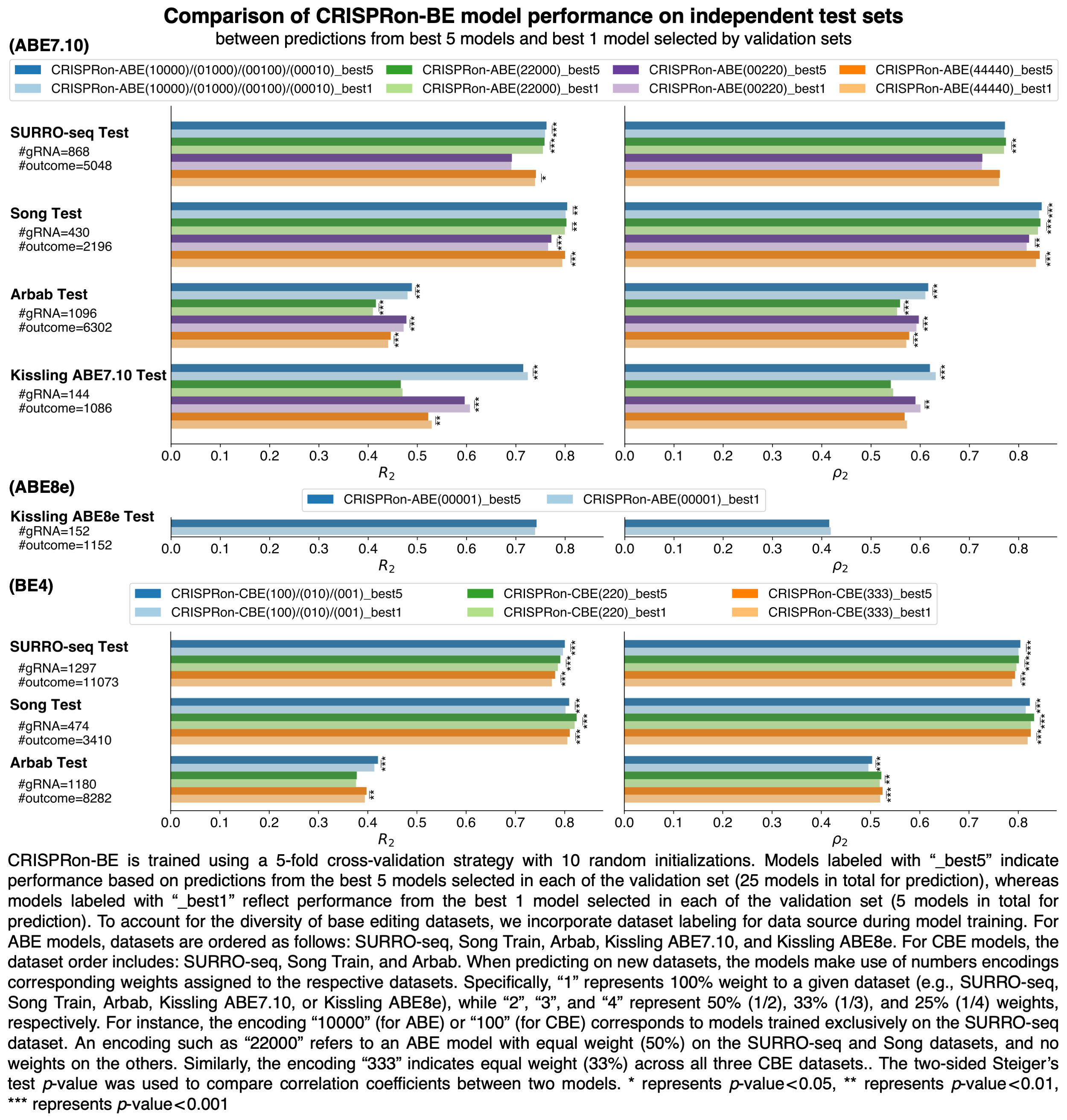
Note, the performance in the webserver is slightly different from the performance reported in the manuscript. CRISPRon-BE is trained using a 5-fold cross-validation strategy with 10 random initializations. In the manuscript, the performance is based on the average of the output from the best five models chosen for each fold (25 models in total for prediction). But in the webserver, the performance is based on the average of the output from the best model chosen for each fold (5 models in total for prediction) to optimize webserver speed. The detailed performance comparison is available here
Citing CRISPRon-BE
If you are using the results of the CRISPRon-BE in your publication, please cite:
Deep learning models simultaneously trained on multiple datasets improve base-editing activity prediction
Sun Y, Qu K, Corsi GI, Anthon C, Pan X, Xiang X, Jensen LJ, Lin L, Luo Y*, Gorodkin J*
Nat Commun. 2025 Nov 7;16(1):9821
[ PubMed | Paper | Webserver | Software ]
Feedback
We greatly appreciate your comments. Open Feedback form in a new tab. Alternatively you can E-mail us with your questions and comments.