CRISPRon(v1.0): CRISPR-Cas9 guide efficiency prediction
Help
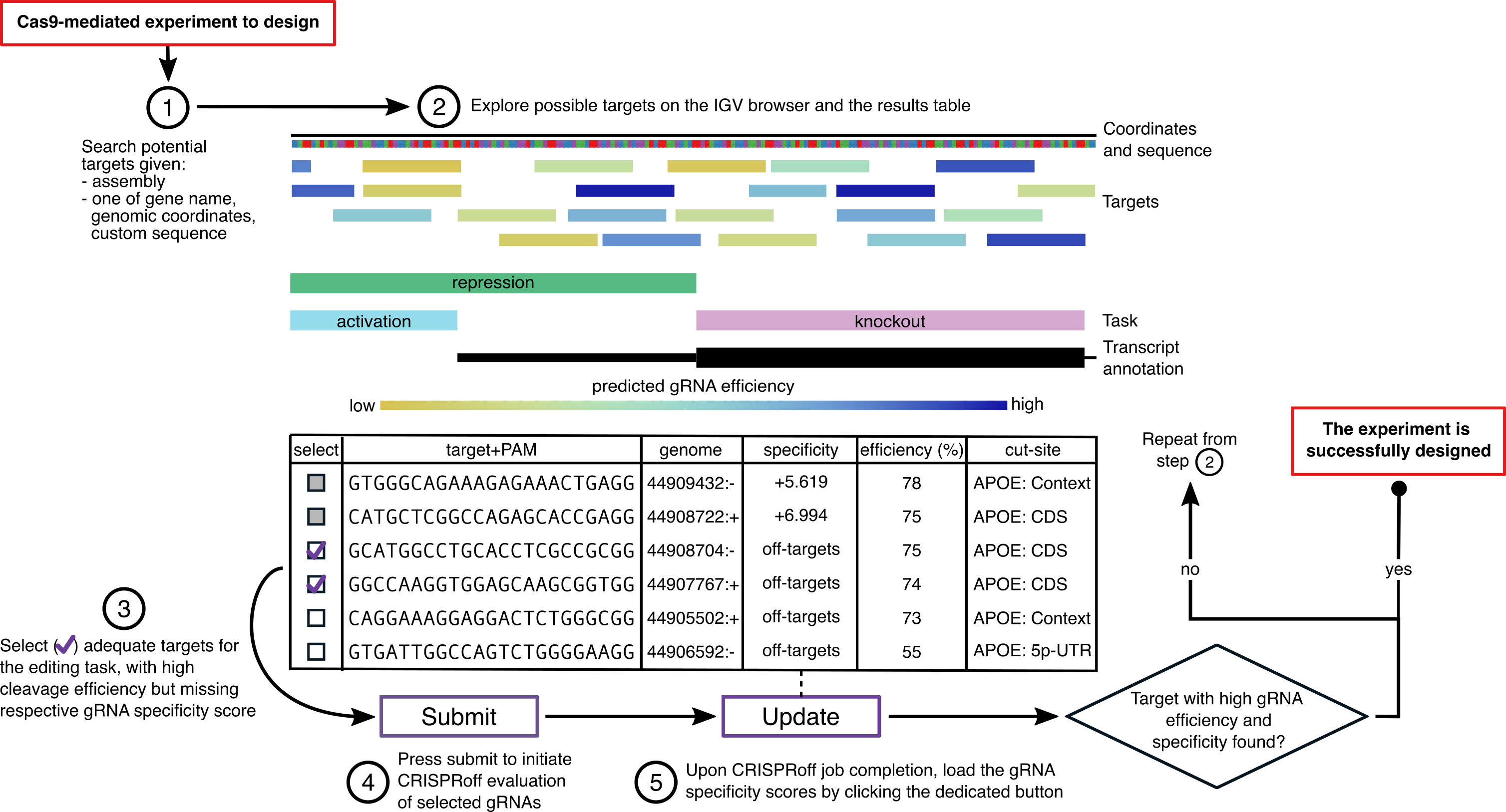
The CRISPRon webserver is dedicated to the design of guide RNAs (gRNAs) for the CRISPR/Cas9 system. The CRISPRon model predicts the efficiency of CRISPR/Cas9-gRNAs in cleaving a target site on the DNA (on-target). Using the webserver, you can find possible CRISPR/Cas9 targets from an input sequence and obtain the predicted Cas9 cleavage effiency of the matching gRNA (indel frequency obtained at approx. 3 days after gRNA delivery).
Once potential gRNAs and corresponding target sites have been selected in CRISPRon, they can be submitted to our webserver for off-target assessment CRISPRoff directly from the CRISPRon results page (visit the CRISPRoff webserver for more info on off-targets). The gRNA specificity score computed by CRISPRoff, which is a measure of how well the gRNA binds to its on-target considering possible genome-wide off-targets, is imported the CRISPRon results page for a final selection of the gRNAs. We recommend to select gRNAs with maximum predicted efficiency and specificity. Note that the sequences reported as "targets" are the same of the gRNAs plus the PAM: targets are here written in 5'-3' direction as the gRNAs, while the actual strand targeted by the gRNA is the opposite (3'-5').
The webserver can be used with three different kinds of input: a genomic range, a gene name, or a custom input sequence. For the first two cases a target genome must be specified, while for the latter the given sequence may or may not map to a target genome.
Format for INPUT-1: Targeting a genomic region
First, select one of the listed genomes in the drop down menu. If the genome you are interested in is not listed, please use the "Format for INPUT-3" described below. Then, type in a genomic region in the dedicated form, and press submit. The genomic region should be specified in the following format: chrN:start-end, where chrN is the identifier of the chromosome, and start/end mark the genomic range, as in the example below.
chr5:73,164,226-73,170,298
Format for INPUT-2: Targeting a gene
First, select one of the listed genomes in the drop down menu. Then, select a gene in the form by typing its name (a drop-down menu will appear after 3 characters), and press submit. In this mode, only exons (coding exons or UTRs) will be considered as targets. If you wish to target introns you must use one of the other input options. If either the genome or the gene is not listed, you should use the "Format for INPUT-3" and manually enter your target sequence as explained below. In addition to targets in exons, targets in the 300 nt sequence up-stream and down-stream of each transcript are also shown in the output. Input example:
SLC10A4
Format for INPUT-3: Targeting a custom input sequence
Paste-in a target DNA sequence in plain or in fasta format as shown in the examples below and press submit. If your sequence is from one of the organisms listed in the drop down menu, it is recommended to select that organism in the form, even if your input sequence doesn't map perfectly to the target genome.
Example of sequence in plain:
ATCGTTGCGTACGGTACGTCCTGACGTAGGGCACGCTCGATCGAGTTCGGACCTGTAGGGATCGAGGCTTGTACGGACC TCACGATCGATCCCGATCGGAATGC
Example of sequence in fasta format:
>myseq_id ATCGTTGCGTACGGTACGTCCTGACGTAGGGCACGCTCGATCGAGTTCGGACCTGTAGGGATCGAGGCTTGTACGGACC TCACGATCGATCCCGATCGGAATGCHint: how to get a DNA sequence. A possible way to obtain the DNA sequence of a given region or gene is to search for it in the UCSC genome browser and then use View->DNA. If the region contains a mutation in your subject, edit the sequence accordingly before submitting it to CRISPRon (see "Examples of input/output" below).
Input criteria. The input must contain only the following five canonical bases 'A,a', 'C,c', 'G,g', 'T,t' and 'U,u' or unknown bases 'N,n'. Targets that include unknown bases are omitted from the output. Predictions are made for a possible target site only if at least 30 nt made of 4 nt + target (20 nt) + PAM (NGG) + 3 nt are present in the given sequence.
Email and custom job name
It is not necessary that you provide an email address or a custom job name. If you do provide an email address we will inform you by email when the computation for your job finishes. The email will include the optional job name (if specified, "crispron" otherwise) and a link that you can use to access the results for your job. The results are stored on the server for 14 days; after that, your results and your email address are deleted from the server.
Examples of input/output
Here we show the input-output for a search done using a custom sequence mapping in part to the human genome assembly hg38. The output for the other input types is similar, but extra care is needed when the input sequence is different from the reference assembly.
Input
For this example we input a custom sequence, which consists in a portion of the IGF1R gene carrying the rs1409058783 G>A mutation at position chr15:98707586. The DNA sequence in a region of 100 nt left and right the mutation (below shown in bold) was retrieved from the UCSC and manually edited as follows:
Wild-type sequence:CTGTATTATTGTTTGGAAAATAGTTTAAAAATTATTTCCTTCTAACTGAGACGTTTACCCTCTTGTCTCCCTTCAGTCT GCGGGCCAGGCATCGACATCCGCAACGACTATCAGCAGCTGAAGCGCCTGGAGAACTGCACGGTGATCGAGGGCTACC TCCACATCCTGCTCATCTCCAAGGCCGAGGACTACCGCAGCTACSequence carrying rs1409058783 G>A mutation:
CTGTATTATTGTTTGGAAAATAGTTTAAAAATTATTTCCTTCTAACTGAGACGTTTACCCTCTTGTCTCCCTTCAGTCT GCGGGCCAGGCATCGACATCCACAACGACTATCAGCAGCTGAAGCGCCTGGAGAACTGCACGGTGATCGAGGGCTACC TCCACATCCTGCTCATCTCCAAGGCCGAGGACTACCGCAGCTAC
As explained above, the input is provided to the webserver by selecting the hg38 genome and pasting the target sequence in the appropriate field.
>hg38_dna CTGTATTATTGTTTGGAAAATAGTTTAAAAATTATTTCCTTCTAACTGAGACGTTTACCCTCTTGTCTCCCTTCAGTCT GCGGGCCAGGCATCGACATCCACAACGACTATCAGCAGCTGAAGCGCCTGGAGAACTGCACGGTGATCGAGGGCTACCT CCACATCCTGCTCATCTCCAAGGCCGAGGACTACCGCAGCTAC
Output
The output consists in an interactive view implemented in the IGV (Integrative Genoimc Veiwer) browser and a table of results, in which details are reported, by default, for each predicted target that can be cleaved with efficiency >= 50%. To see the results on the UCSC genome browser instead, click on "View in UCSC". The results can also be downloaded as a zip folder by clicking on "Download results". The folder will include the results table in csv format and bed files of the predicted targets. Note: you can open the csv table in Excel, just remember to save it as xlsx (Excel file) if you edit it with colors, font changes, filters etc. To see the results on the UCSC genome browser instead, click on "View in UCSC".
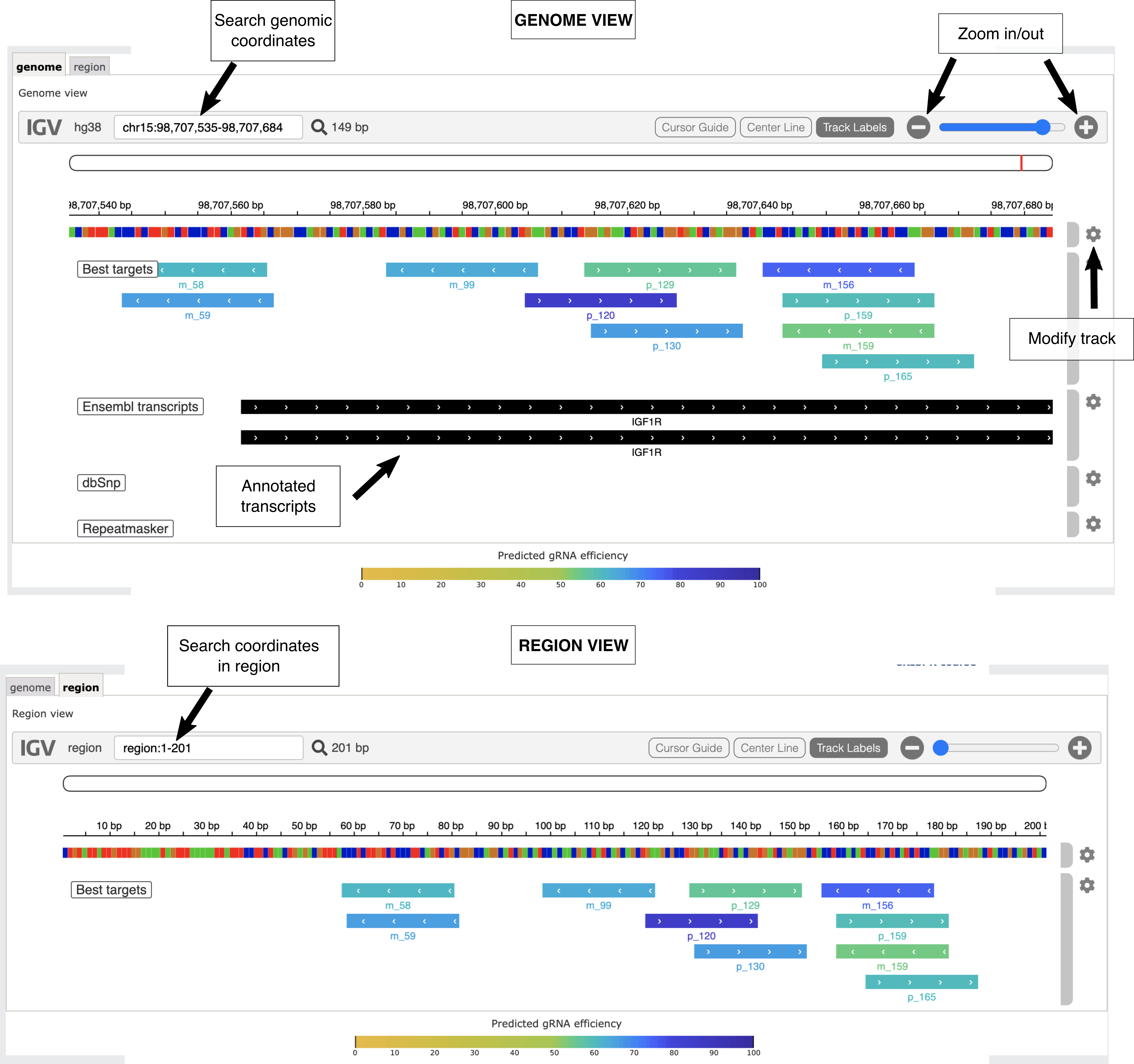
The IGV interactive view
An example of the IGV browser view is displayed in the figure below, where the genome view is at the top and the region view is at the bottom. The genome view is relative to where your custom sequence maps in the genome, while the region view is relative to your custom sequence. You can switch between views by clicking on the tabs located in the top left margin of the IGV view.
In IGV you can:- zoom in and out: click on the +/- buttons
- move left and right: click on the view and drag the mouse
- move/zoom to a sub-region by coordinates: type in the coordinates in the dedicated field. The coordinates can be specified respctive to the genome or within the region, depending on the view you are in.
- visualize annotated transcripts. Thick black bars represent the exons (less thick in UTRs, thicker in the coding sequences). The interconnecting fish-bone lines denote the introns. The directionality is given by the arrows on the bars and lines. Click on the annotation to get further information (identifiers, coordinates...)
- see the annotations on the best regions for activation, repression, and knockout (not available for custom sequence query)
- see SNPs annotated in dbSNP (only human)
- see repeatmasked regions (bottom track).
- modify the tracks (squish genomic annotations, show the amino-acid translation frame...): click on the settings icons at the right border of the view
Target regions, which represent potential gRNAs, are represented by horizontal coloured bars. The efficiency is reflected in the colour of the bar, which follows a colour scale from yellow to blue. The strand of a target is shown by arrows within the bars, as for the genes. Additional information can be obtained by clicking on a bar. Each target has a unique identifier, which takes the form of m_xx or p_xx where m and p signal the strandness (+ or -) and xx represents the start position of the target within the given region.
The options panel
Below the IGV view there is a set of options that allow to choose which targets are shown in the browser view and in the table view. After zooming-in in a certain region, you can click on "Filter" to make the table match the gRNAs in that region. If your table has additional filters (eg. efficiency > 80%) the table may show less targets than the genome browser view.
By default, the option "Targets wit efficiency >= 50% and not repeat sequence" is selected. The option "Targets with efficiency >= 50% for which off-targets have been obtained" is useful only after some gRNAs have been submitted to the off-target webserver (see instructions below).

The table view
The table contains the details about the targets, and allows to filter and sort them depending on their attributes.
To sort the table based on a certain colum, click on one of the triangles next to the column name (triangle pointing up: sort values from bottom to top; triangle pointing down: sort values from top to bottom).
By default, the table is sorted by target coordinates.
You can filter the table by typing a filter in the first row. The table can be filtered by:
- id strand(p/m)_start: the id of a given gRNA
- target+PAM: write the sequence of a motif that you would like your target to contain
- region: start position in the given region
- genome: start coordinates in the current chromosome
- specificity: gRNA specificity score from CRISPRoff. These are not pre-computed, see instructions below "Compute off-targets"
- effciency (%): percentage indel frequency
- cut-site: annotations overlapping the site (coding sequence=CDS, 5' UTR, 3' UTR, Intronic, Intergenic, non-coding exon (NC-exon), Context (the 300 nt up/down-stream the given region added to the search))
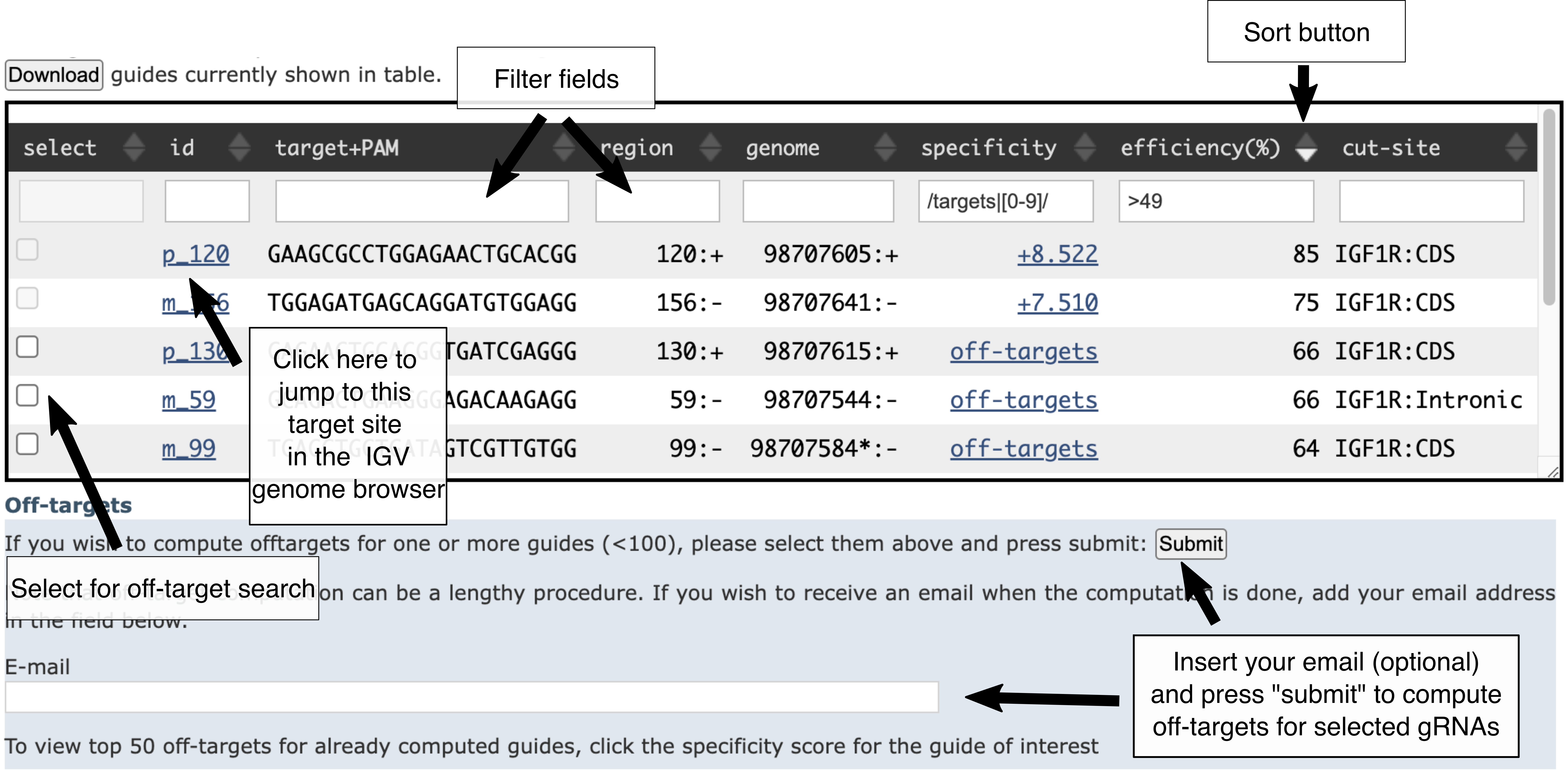
Compute off-targets
By default, specificity scores are notcomputed. This is because computing the specificity of a gRNA is computationally very expensive, as the full genome needs to be searched to find potential off-target sites, which then need to be evaluated. Therefore, the specificity is computed only on-demand for selected gRNAs (targets). Please follow these instructions to obtain the specificity scores:
- select targets by ticking the boxes in the "select" column
- submit the selected targets to CRISPRoff by pressing the "Submit" button. Optional: because the off-target computation can be lengthy (several minutes), you can provide an email, and you will receive a message with a link to the results when the off-target computation is done.
- once the job is completed, press "here" to reload the page. Note that this will remove previous filters and zooms in the browser.
You can now select you target region (which corresponds to the gRNA + PAM sequence) by choosing the gRNA with maximum efficiency and maximum specificity that is suitable for your editing task.
Citing CRISPRon
If you are using the results of the CRISPRon in your publication, please cite:
CRISPRon/off: CRISPR/Cas9 on- and off-target gRNA design
Anthon C, Corsi GI, Gorodkin J* Bioinformatics. 2022 Dec 13;38(24):5437-5439
[ PubMed | Paper | Webserver ]
Enhancing CRISPR-Cas9 gRNA efficiency prediction by data integration and deep learning
Xiang X†, Corsi GI†, Anthon C†, Qu K†, Pan X, Liang X, Han P, Dong Z, Liu L, Zhong J, Ma T, Wang J, Zhang X, Jiang H, Xu F, Liu X, Xu X, Wang J, Yang H, Bolund L, Church GM, Lin L, Gorodkin J*, Luo Y* Nat Commun. 2021 May 28;12(1):3238
[ PubMed | Paper | Webserver | Software ]
Feedback
We greatly appreciate your comments. Open Feedback form in a new tab. Alternatively you can E-mail us with your questions and comments.
